Animals are classified
into microscopic and macroscopic animals. The microscopic animals like
bacteria, amoeba etc have a simple cell structure. The cell contains different
vacuoles. These vacuoles perform specific function. Thus they carry out all the
physiological activities.
The macroscopic animals
are classified into invertebrates and Vertebrates. The Vertebrates are the
animals with the well-developed spinal column, Brain and Nervous System.
Invertebrates do not have vertebral column but they have nerve cells with the
help of which all the sensory activities are carried out. Most of the
invertebrates do not have a well developed brain. Therefore, the invertebrates
cannot recognise sound or interpret sound in their environment. So we
understand that the brain plays a vital role with respect to hearing.
Among the multicellular
animals, Sponges are invertebrates without nervous system. They respond to the
sense of touch by contraction of body. There are no sensory cells for hearing.
Hydra is a multicellular invertebrate animal. They have Nervous system characterised by a network of neurons, concentrated near the mouth. No sensory activities are performed by this organism except eating.
Jellyfish and Sea anemone have interconnected nerve cells all over their body with the help of which they are able to respond to the various types of stimuli of their surroundings.Earthworm has a segmented body. It has brain. They have sense of touch, light and vibration receptors present all over their body. They do not have cells for hearing.Star fishes cannot hear. There is no specific sense organ for hearing. There is no brain also. The nervous system is characterised by nerve ring that surround the mouth. But they have eyespots at the tip of each arm. The eyespot contains light sensitive pigments that allow them to identify shadows and changes in the brightness of the light.Worms like flat worms, round worms, tape worms etc are not capable of hearing or seeing. They move in their environment with help of vibration receptors. They feel the vibrations in their surroundings with the help of these receptors.
Hydra is a multicellular invertebrate animal. They have Nervous system characterised by a network of neurons, concentrated near the mouth. No sensory activities are performed by this organism except eating.
Jellyfish and Sea anemone have interconnected nerve cells all over their body with the help of which they are able to respond to the various types of stimuli of their surroundings.Earthworm has a segmented body. It has brain. They have sense of touch, light and vibration receptors present all over their body. They do not have cells for hearing.Star fishes cannot hear. There is no specific sense organ for hearing. There is no brain also. The nervous system is characterised by nerve ring that surround the mouth. But they have eyespots at the tip of each arm. The eyespot contains light sensitive pigments that allow them to identify shadows and changes in the brightness of the light.Worms like flat worms, round worms, tape worms etc are not capable of hearing or seeing. They move in their environment with help of vibration receptors. They feel the vibrations in their surroundings with the help of these receptors.
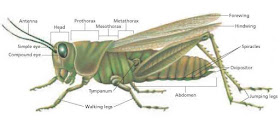
Insects are the only
organisms among the invertebrates that are capable of hearing. Their ears are
located at their head. Their ear drum is a thin part of cuticle sensitive to
air vibrations. Sensitive receptors are located either on the trachea or on the
ear drum.
Insects do not have ears like those of human beings, but are
able to hear through tympanal organs, which work like our ear drum. Insects use sounds to communicate with other
insects, and to navigate in their environment. Some even listen to the sounds
of their predators in order to avoid being eaten. Sound is produced by vibration,
and insects hear by collecting and interpreting the vibrations in their
environment with the help of brain.
Ants don't have
ears. Ants "hear" by feeling vibrations
in the ground through their feet. Ants can detect sounds from other ants
through the air, using hair-like sensors at the tips of their antennae. They
can sense vibrations from the nest, ground, and surrounding leaves using their
antennae. Using this sound, they can locate lost family members and their prey. Many ants produce squeaky sounds by rubbing
one body part against another. They also produce sounds by jaw slapping.




Read Invertebrates Class 10 here
ReplyDelete